MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) provide efficient switching and amplification for power supplies, motor drivers, and signal circuits with high reliability and thermal stability.
Before diving into troubleshooting, it's crucial to understand the basics. MOSFETs, or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors, are used to amplify or switch electronic signals. They are favored for their efficiency and are prevalent in various electronic devices.
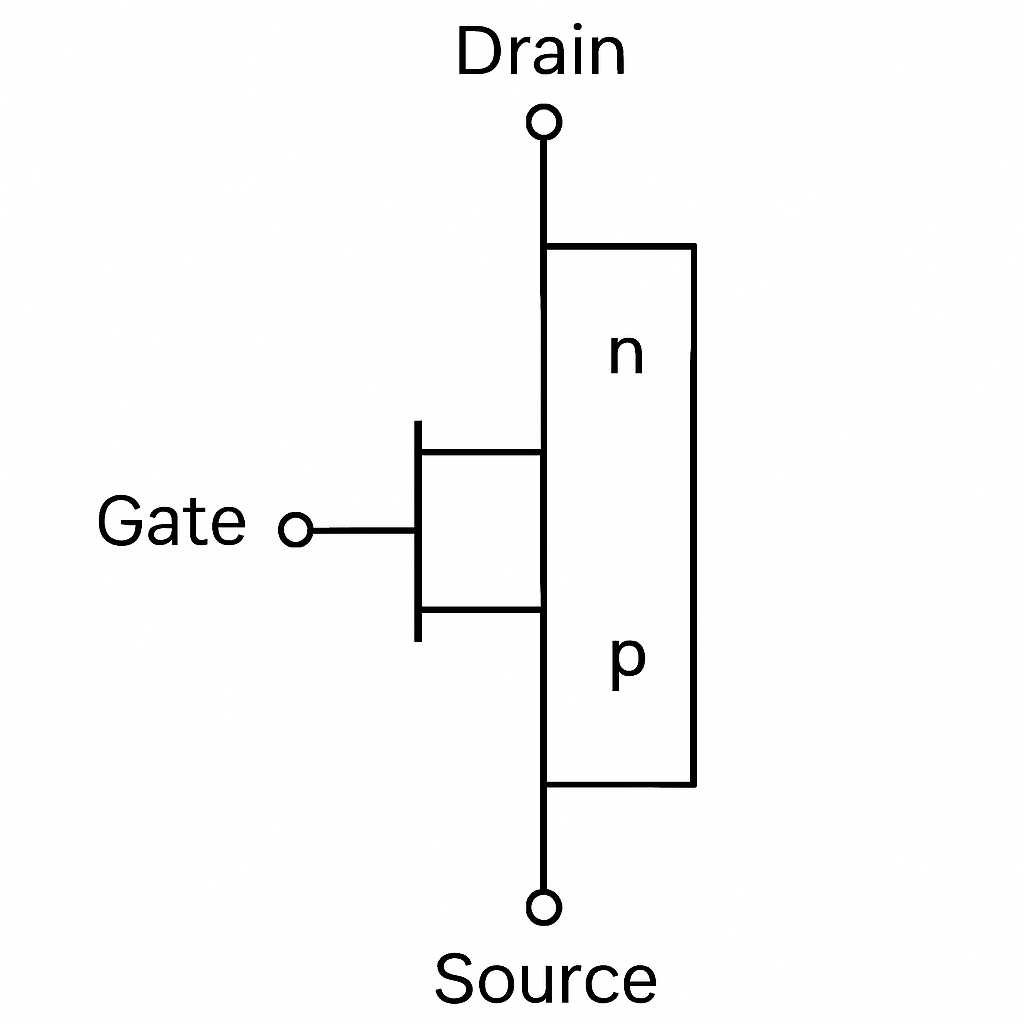
Structure and Functionality
MOSFETs have a unique structure comprising three terminals: the gate, drain, and source. The gate terminal controls the flow of current between the drain and source. This mechanism allows MOSFETs to function efficiently as switches or amplifiers. Understanding the role of each terminal is crucial for troubleshooting and circuit design.
Types of MOSFETs
MOSFETs come in two main types: N-channel and P-channel. N-channel MOSFETs are generally used for low-side switching, while P-channel MOSFETs are used for highside switching. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the right MOSFET for your circuit. Each type has distinct characteristics that impact how they should be implemented within electronic circuits.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The primary advantage of MOSFETs is their high efficiency and fast switching speed. These traits make them invaluable in applications like power supplies and motor controllers. However, MOSFETs are sensitive to static electricity and require careful handling. Knowing these pros and cons can assist in making informed decisions during circuit design and troubleshooting.
Common MOSFET Circuit Issues

Now, let's delve into some common issues you might face with MOSFET circuits and how to troubleshoot them.
Overheating
One of the most common issues is overheating. MOSFETs can generate a lot of heat, which, if not managed properly, can lead to failure. Ensure that your MOSFET has proper heat sinking and ventilation to dissipate the heat effectively. Additionally, consider the ambient environment and whether external cooling methods, like fans, might be necessary.
Incorrect Gate Voltage
The gate voltage controls the MOSFET's ability to switch on and off. An incorrect gate voltage can prevent the MOSFET from functioning correctly. Verify that the gate voltage is within the specified range for your MOSFET type. Double-check the power supply and signal sources to ensure they are delivering the appropriate voltage levels.
Misfiring
MOSFET misfiring can occur due to noise or interference. To mitigate this, use proper filtering techniques and ensure that your circuit layout minimizes inductance. Shielding and grounding can also play significant roles in reducing noise and preventing misfiring. Evaluate the circuit for potential sources of electrical noise and address them accordingly.
Logic Level MOSFET Issues
Logic level MOSFETs are designed to be driven by lower voltages, like those from microcontrollers. If a logic level MOSFET isn't switching properly, check the logic voltage levels and ensure they are suitable for the MOSFET's requirements. Also, examine the microcontroller's output capabilities and consider using a driver circuit if necessary to boost the control signal.
MOSFET Characteristics and Applications
Switching Characteristics
MOSFETs are known for their fast switching capabilities. They can turn on and off rapidly, which makes them ideal for applications like power supplies and motor drivers. If your MOSFET isn't switching as expected, check the gate capacitance and ensure it matches the application's needs. Consider the impact of parasitic capacitance and how it might affect switching speeds.
Thermal Characteristics
Thermal management is crucial in MOSFET applications. Ensure that your MOSFET is operating within its thermal limits by using adequate heat sinks and considering ambient temperature effects. Investigate different thermal interface materials and techniques to enhance heat dissipation and prolong the MOSFET's lifespan.
MOSFET Applications
MOSFETs are used in a variety of applications, from power electronics to signal processing. They are an integral part of DC-DC converters, amplifiers, and more. Explore different application scenarios to understand how MOSFETs can be leveraged for optimal performance. This knowledge can guide you in troubleshooting specific application-related issues.
Troubleshooting Tips
When troubleshooting MOSFET circuits, keep these tips in mind:
Conclusion
Troubleshooting MOSFET circuit issues requires a good understanding of MOSFET basics and characteristics. By knowing common issues and how to address them, you can ensure your circuits run smoothly and efficiently.
MOSFETs are powerful components that, when used correctly, offer significant advantages in various applications. Whether you're dealing with overheating, gate voltage issues, or misfiring, the key is to approach each problem methodically and refer to technical resources as needed.
With these tips and insights, you're well on your way to mastering MOSFET circuits and overcoming any challenges that arise. Happy troubleshooting!
Power MOSFET | Fast Switching Transistor | Reliable Motor & Power Supply Driver