Explore the key electrical characteristics of aluminum electrolytic capacitors: nominal capacitance, leakage current, equivalent series resistance (ESR), ripple current, impedance, and dissipation factor (Tanδ). Ideal for selection and design in high-performance power, industrial, and automotive electronics.
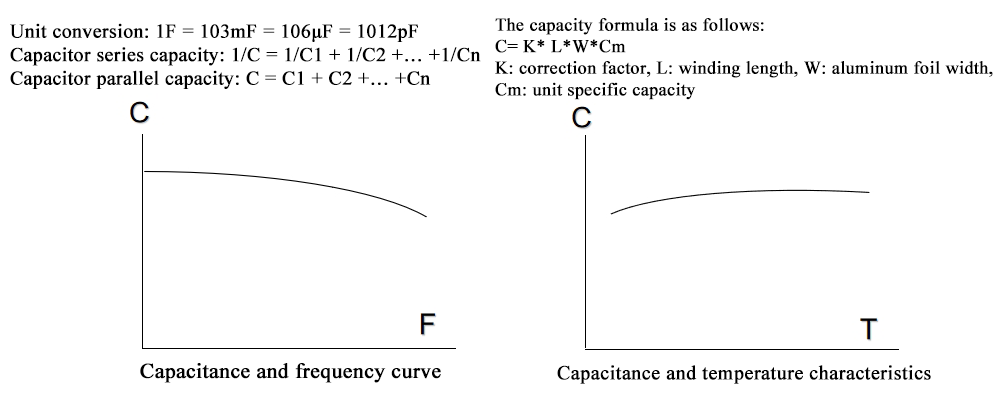
Capacitor electrical characteristics - nominal capacity (μF):
Nominal Capacitance (μF): refers to the capacitance value marked on the capacitor, which refers to the number of charges stored per unit voltage and is the nominal value of the designed capacity. The actual capacity of the capacitor will vary within the specified tolerance. (The default tolerance is ±20%)
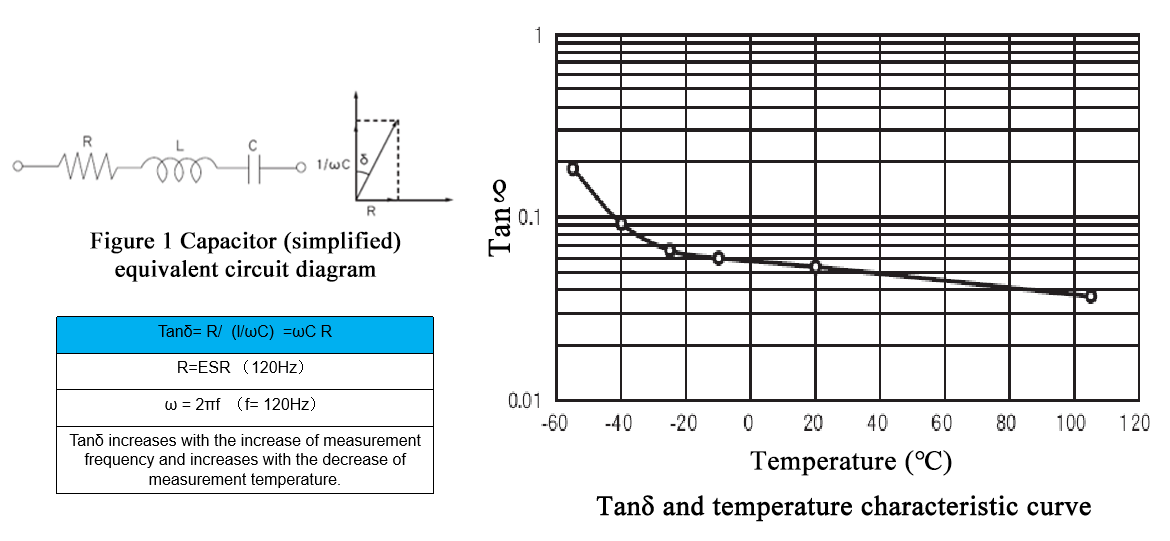
Capacitor electrical characteristics—Tanδ (DF value)
Tanδ: The figure is a simplified equivalent circuit diagram of a capacitor. The equivalent circuit resistance of an ideal capacitor is R=0, Tanδ=0. However, in reality, due to the presence of electrolyte, electrolytic paper and other contact resistances, in the equivalent circuit, the ratio of the equivalent series resistance ESR to the capacitive reactance 1/ωC.
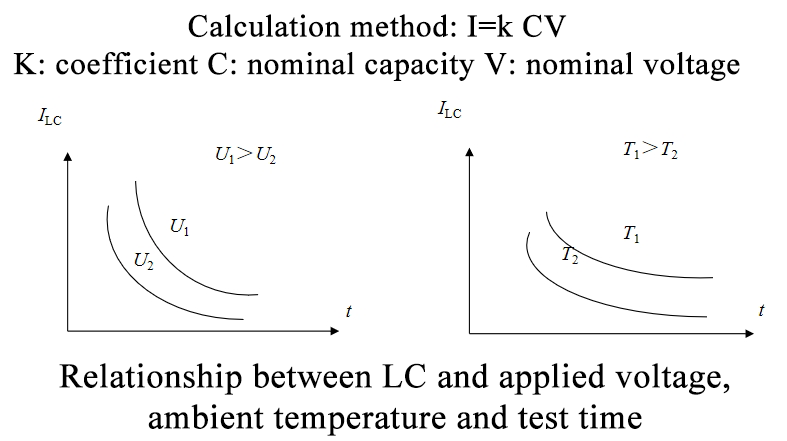
Capacitor electrical characteristics—LC (leakage current)
Leakage current (μA): Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are subjected to working voltage and the leakage current is measured after a specified period of time by testing the leakage current passing through the capacitor. This characteristic is mainly used as an indicator parameter to characterize the insulation characteristics of the oxide film of electrolytic capacitors.
Capacitor electrical characteristics-ESR
ESR (Ω): refers to the equivalent series resistance of the electrolytic capacitor, which is the main factor affecting the heat generation of the capacitor during operation.
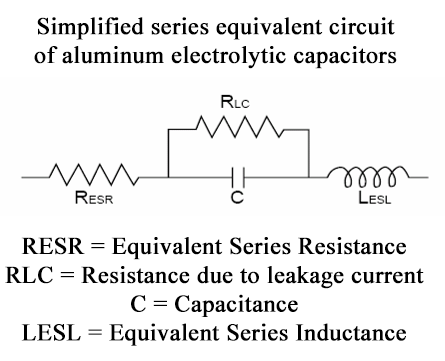
Equivalent series resistance ESR (Ω) is a value that characterizes the total ohmic loss of a capacitor. In the equivalent circuit, it is connected in series with the capacitance. It comes from the resistance of the electrode foil, electrolyte, lead wire and the connection resistance between them.
Conversion relationship with Tanδ: ![]()
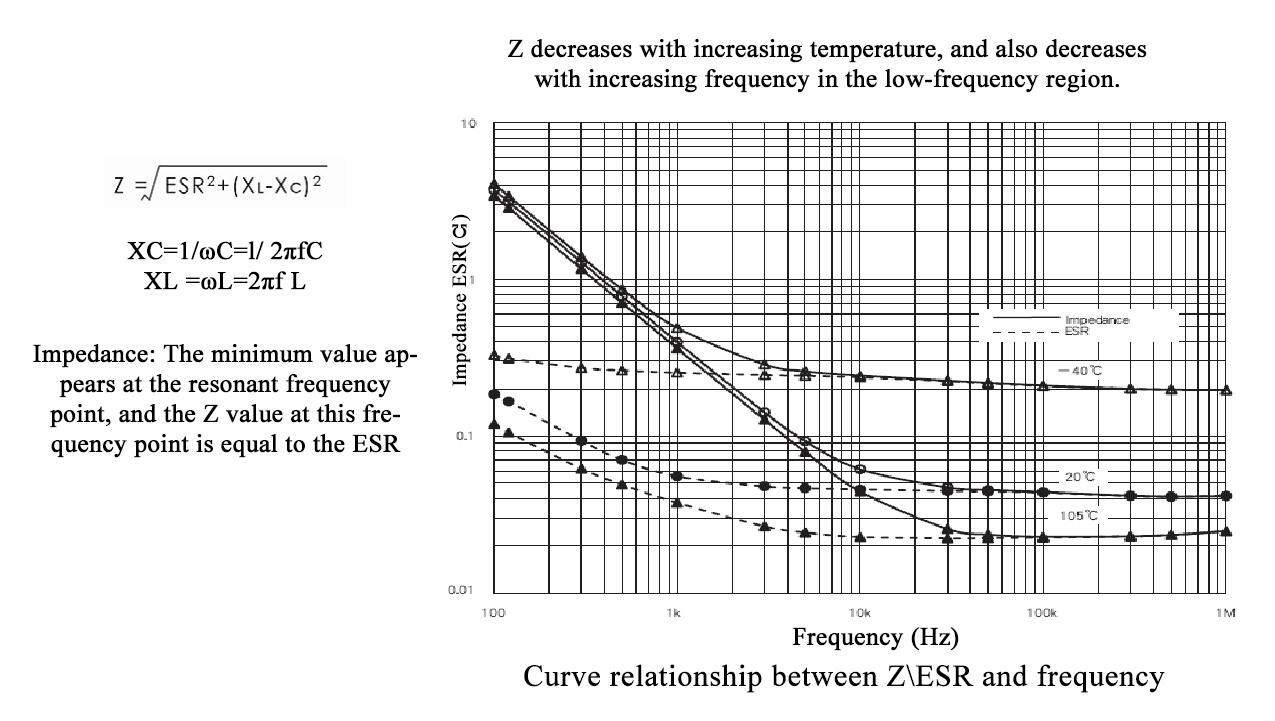
Capacitor electrical characteristics--Z
Impedance Z (Ω): At a specific frequency, the resistance that blocks the passage of alternating current is called impedance (Z). It is related to the capacitive reactance and inductive reactance corresponding to the capacitance and inductance, and is also related to the equivalent series resistance ESR. The specific expression is as follows:
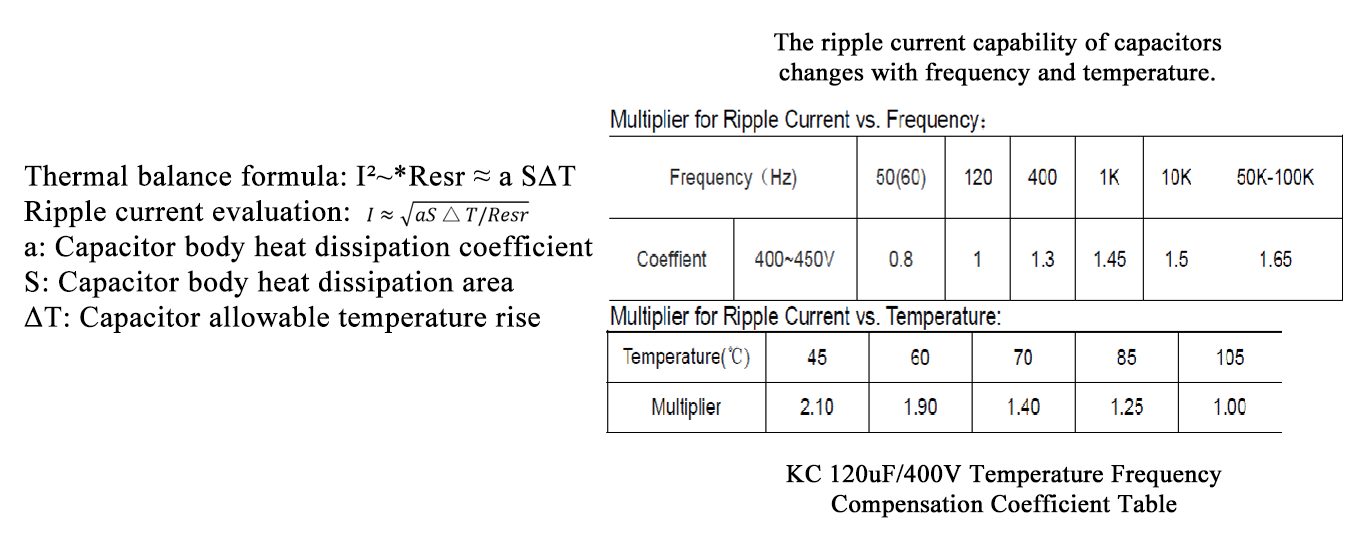
Capacitor electrical characteristics—R.C (ripple current)
Ripple current (mA rms): The working voltage of aluminum electrolytic capacitors is a DC component with an AC component voltage of different frequencies superimposed on it. In this case, the AC current flowing through the capacitor is called ripple current. Ripple current is the main factor causing the capacitor to heat up. Since the ability of aluminum electrolytic capacitors to withstand ripple voltage is closely related to factors such as the frequency of the superimposed ripple current, the nominal ripple current of capacitors is generally marked with the operating frequency, so special attention should be paid to the selection.
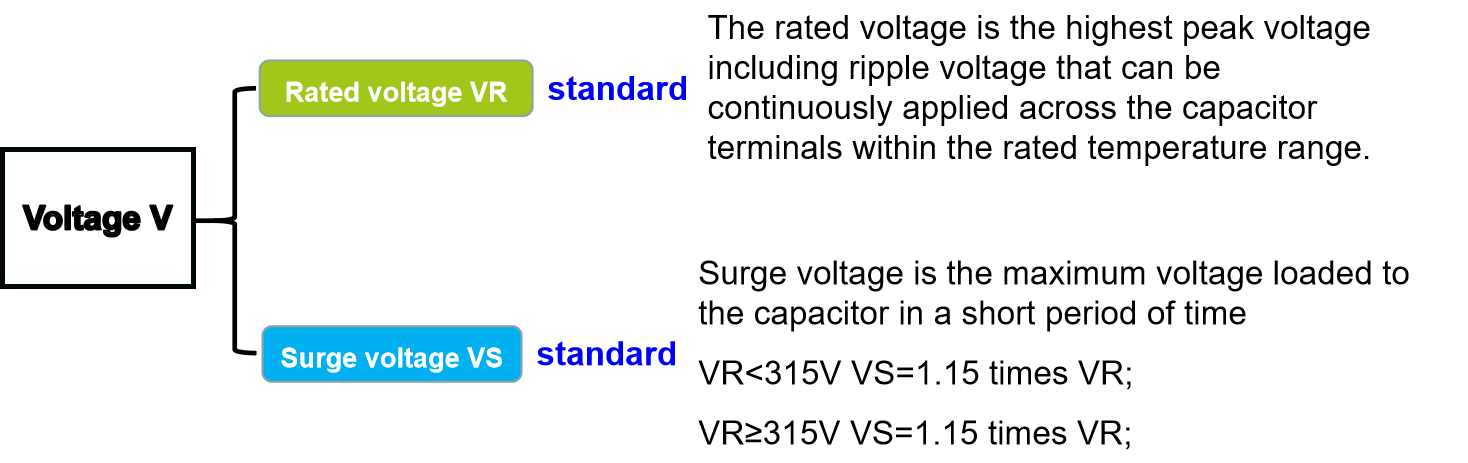
Capacitor electrical characteristics - voltage