Discover the essential differences between X and Y safety capacitors, their roles in suppressing EMI, and why certified components are critical for AC circuit protection. Learn about placement, function, dielectric materials, and voltage ratings in detail.
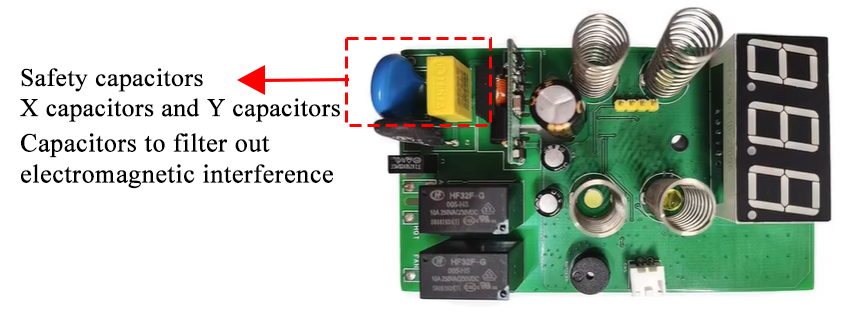
In AC-powered electronics (especially 220V/230V mains), safety capacitors are often used on the input side. They are commonly color-coded:
Yellow = X capacitors (line-to-line)
Blue = Y capacitors (line-to-ground)


1. What Are Safety Capacitors?
“Safety capacitors” are certified components designed to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure safe failure behavior (no shock or fire) under mains voltage.
There are two main types:
X capacitors – Between Line (L) and Neutral (N)
Y capacitors – Between Line/Neutral and Ground (PE)
Note: These are classified by function and safety certification, not by dielectric material.
2. Functional Differences: X vs. Y Capacitors
|
Feature |
X Capacitor |
Y Capacitor |
|
Function |
Filters differential mode noise |
Filters common mode noise |
|
Placement |
Between Line (L) and Neutral (N) |
Between Line/Neutral and Ground (PE) |
|
Noise Type |
High-frequency signals with opposite phase |
In-phase high-frequency signals |
|
Dielectric |
Metallized polypropylene film |
Multilayer ceramic |
|
Voltage Rating |
250–310VAC (Class X1/X2) |
Up to 4000V+ (Class Y1/Y2) |
3. Why Ordinary Capacitors Cannot Replace Safety Capacitors
● General capacitors lack safety certifications
● May short or catch fire upon failure
● Many are polarized and unsuitable for AC
● X capacitors cannot replace Y capacitors due to safety demands in ground-referenced circuits
4. Key Takeaways
● X capacitors are used to suppress differential-mode interference.
● Y capacitors are used to suppress common-mode interference.
● X capacitors typically have higher capacitance than Y capacitors, but a lower voltage rating.