This article introduces the structure, type differentiation, industry applications, and future trends of RF coaxial connectors, serving as a selection guide for engineers in telecom, automotive, radar, and more.
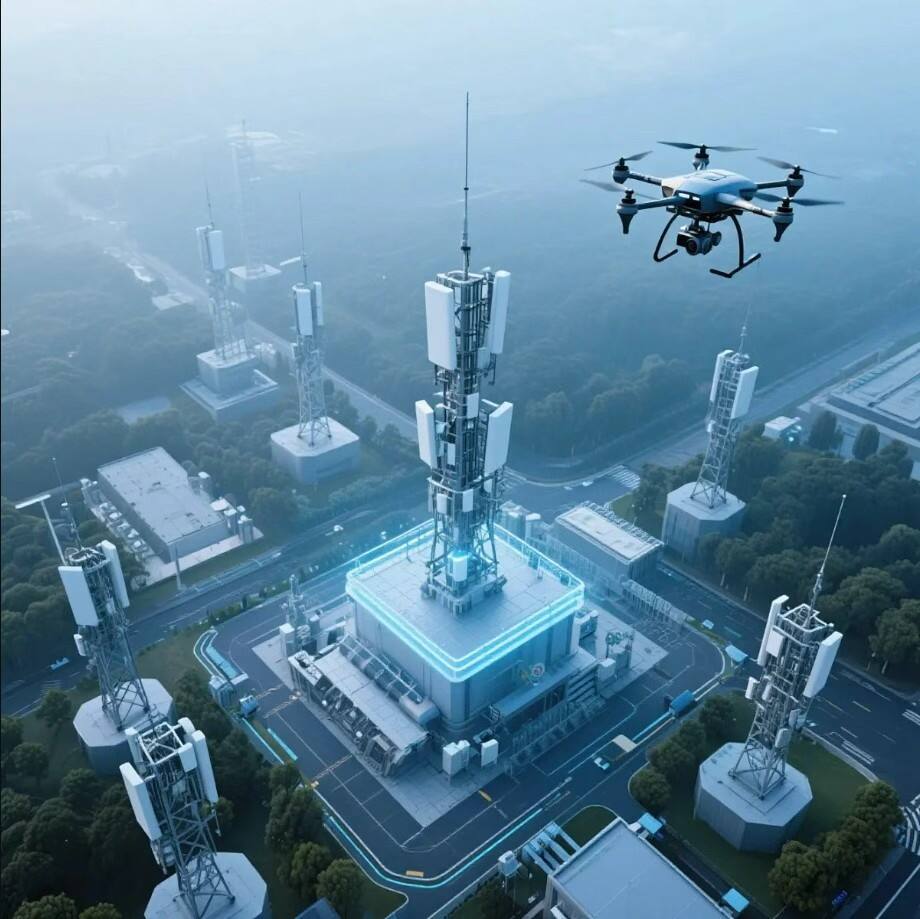

I. Structure and Working Principle of RF Coaxial Connectors
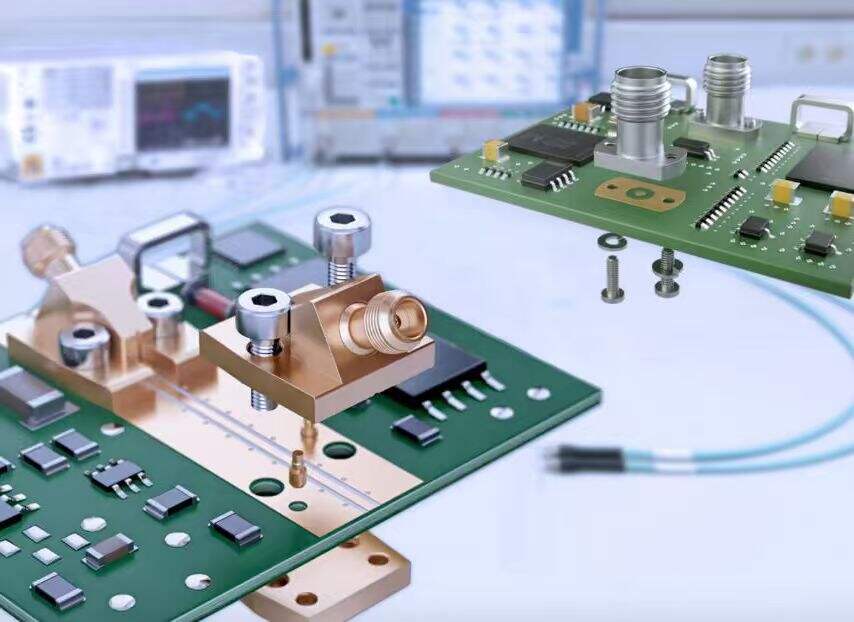
RF coaxial connectors are electrical connectors designed for radio frequency signal transmission. They consist of an inner conductor, dielectric insulation, and an outer metallic shield, ensuring low loss and high-fidelity signal delivery.
Common impedance values include 50Ω and 75Ω, catering to various RF system requirements.
II. Common Connector Types and Applications
SMA Connectors: Threaded structure, frequency up to 18GHz, widely used in base stations and microwave communication.
BNC Connectors: Quick plug-in type, commonly found in video surveillance and broadcasting systems.
SMB/TNC Interfaces: Suitable for compact devices like navigation modules and automotive radars.
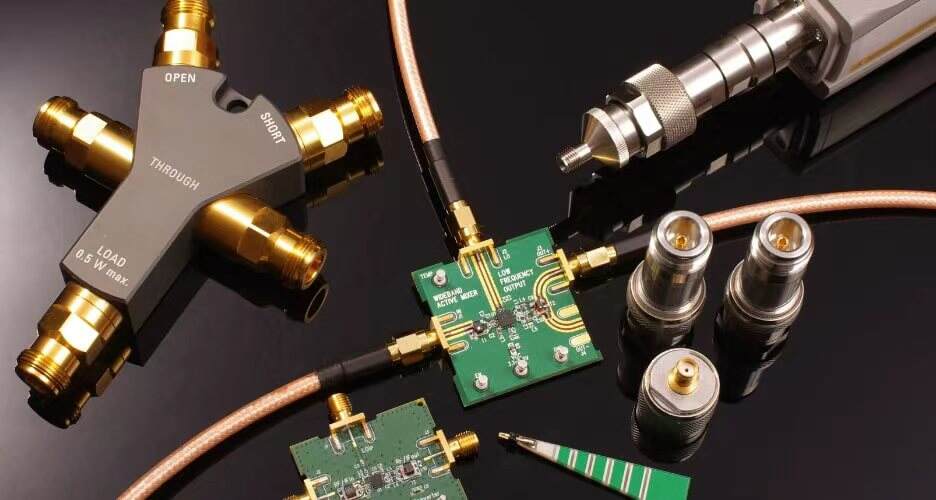

III. Industry Application Scenarios
IV. Advantages of RF Coaxial Connectors
V. Technical Trends and Development
With the advancement of millimeter wave, smart vehicles, and high-density communication equipment, RF connectors are trending toward higher frequencies, miniaturization, and module-level integration.
Future designs will focus on integration with antennas, filters, and PCBs, enabling lower-loss and higher-performance systems.
RF Plug | High Frequency Connector | Communication RF Adapter | SMA Port | BNC Jack